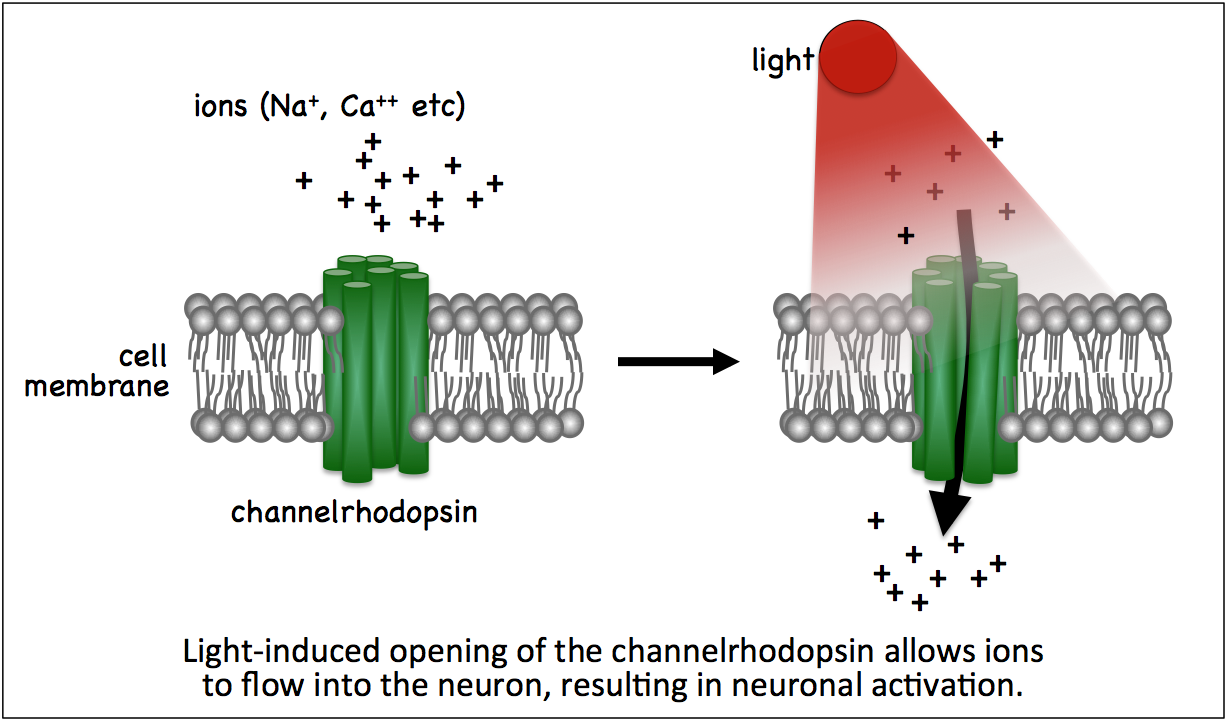
'Optogenetics' refers to techniques used to control cells in living organisms with light. The main optogenetic tools currently in use utilize light-activated channelrhodopsins from green algae to activate neurons. By expressing a channelrhodopsin in subsets of neurons, one can study the specific behaviors controlled by those neurons by shining light of a specific wavelength (the wavelength depends on the channelrhodopsin used) to open the channelrhodopsin and activate the nerves (see below).
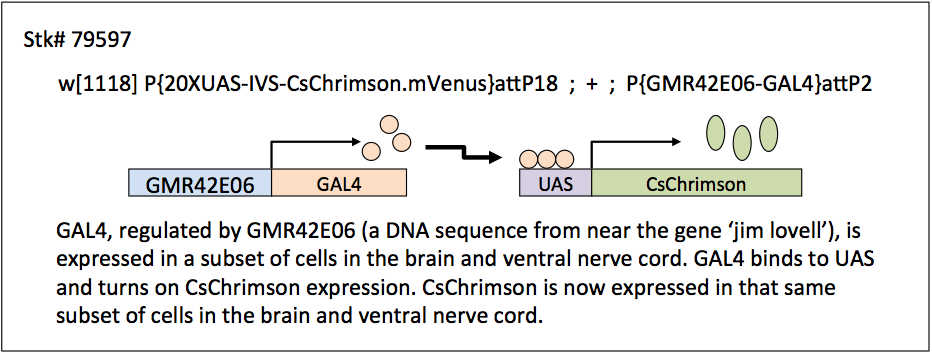
Ilya Vilinsky (University of Cincinnati), Karen Hibbard (Janelia Research Campus), Bruce Johnson and David Deitcher (Cornell University) have developed a set of stocks and student lab exercises that demonstrate optogenetic techniques in Drosophila melanogaster. These stocks utilize the GAL4/UAS system to express a channelrhodopsin in subsets of neurons in either larval or adult flies (see schematic below for an example of how the GAL4/UAS system works). By shining either an intense red (625 nm) or blue (460 nm) light onto animals fed all-trans retinal (a co-factor necessary for making a functional channel), the channelrhodopsins open and the neurons expressing these proteins are depolarized and activated, resulting in a specific behavior.
Activation of channelrhodopsins in these stocks can be achieved using inexpensive handheld red light (for CsChrimson) or blue light (for H143R-ChR2) flashlights made by companies like JOYLIT or WAYLLSHINE (look for 465 nm or 620 nm tactical CREE XP-E LED flashlights - you'll want a light with at least 200 lumens). You will need to include all-trans retinal in the fly food. Karen Hibbard says "We suspend [all-trans retinal] in ethanol to make a 100 mM stock solution. You can then make vials with a 1:500 dilution in fly food for a final concentration of 0.2 mM. It doesn’t completely dissolve, just resuspend as much as possible. I would suggest making aliquots and storing in the freezer. These stock solutions should last indefinitely. The retinal is light sensitive so avoid strong white light and cover with foil when possible."
For more information on these lines and their uses, please see Vilinsky et al., 2018. For a lab utilizing two of the lines, please download the CrawFly Workshop 'Optogenetically Induced Adult Behaviors' lab instruction sheet.
If you have questions, please contact Dr. Karen Hibbard.

